Although frequently used as a synonym, virtualization and cloud computing radically differ from one another. Virtualization is the software that allows one physical server to run several individual computing environments. It entails the optimization of computing resources that are key to deliver cloud services. But cloud computing isn’t virtualization alone. It’s in essence much more dynamic and strategic, as it focuses on the services that can be delivered regardless of the deployment model (hybrid, private, public)
Here are some of the key differences between virtualization and cloud computing:
Tactical vs. Strategic
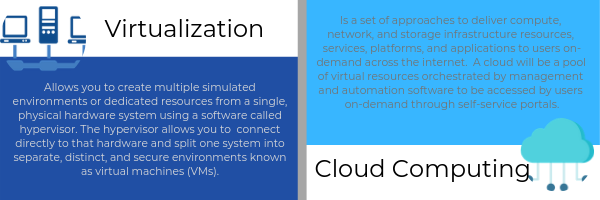
In the early 2000s, businesses were looking for a way to optimize their computing resources, avoiding the investment on additional servers to keep up the demands. Virtualization was then conceived, as a tactical way to partition resources on a server to create multiple simulated environments from one physical hardware system.
On the other hand, Cloud Computing is considered to be a more strategic decision as it involves services that share a pool of automated virtual resources for on-demand use. Meaning that the business needs to make a strategic decision as to which services they want to consume on a cloud basis that will have a direct impact on business processes and efficiency. The business benefits of cloud computing have a direct impact on key business performance and growth metrics, this is why it needs to be considered as a business strategic decision.
Packaged Resources vs. Variable Services
Virtualization delivers packaged resources to specific users for a particular purpose. Businesses experience great cost-savings by purchasing and maintaining fewer servers that have a greater computing capability.
When virtualizing your environment, you can divvy up the resources of a single physical server to create several separate virtual environments, called virtual machines. A virtual machine (VM) is an isolated software container with an operating system and applications inside. By design each self-contained VM operates completely independent, allowing many of them to run simultaneously on a single computer.
Cloud Computing delivers variable resources/services to groups of users for a variety of purposes all through the internet. With cloud computing, you’re no longer thinking of computing resources, but services. From basic storage to cloud applications these services need to be orchestrated and automated for quick implementation.
Optimization vs. Automation
By nature, both technologies are looking to optimization resources and achieve a higher level of automation. However, the approach they take to resources and services makes them have a clear and different primary goal.
While Virtualization’s main objective is to optimize the server utilization bringing unprecedented simplicity, speed and flexibility to IT provisioning and management, cloud computing takes this one step further by considering automation as key to high-performance provisioning on-demand access to the services in the catalog in a faster matter.
This doesn’t mean that virtualization doesn’t deem automation important; in fact, virtualization management tools typically include intelligent automation capabilities. These tools eliminate the need for IT workers to perform routine maintenance and troubleshooting on multiple physical machines manually. But, for a cloud computing deployment to be successful automation must be at the center of priorities, it must include workload moves, resource scaling, backup and disaster recovery, and application lifecycle management. The bottom line is this: cloud run-time management requires automation, especially for all those time-consuming, error-prone maintenance activities that are essential for efficient and reliable cloud service delivery.
There you have it, two equally buzz-worthy technologies, and three key differences. Virtualization is, in essence, a software that makes computing environments independent of physical infrastructure, while cloud computing is a service that delivers shared computing resources/services (software and data) on demand via the Internet. They are, however, complementary solutions, and are part of IT transformation projects. Organizations can begin by virtualizing their servers to optimize their resources, and then migrate to cloud computing for even greater agility, automation, and self-service.
 Download VMware e-Book Virtualization Essentials
Download VMware e-Book Virtualization Essentials
Virtualization is becoming an attractive alternative for businesses of all sizes seeking to boost their business agility as they simplify IT operations, improve business continuity, and minimize risks.
Virtualization relies on software to simulate hardware functionality and create a virtual computer system. This enables IT organizations to run more than one virtual system and multiple operating systems and applications - on a single server. Learn more in this e-Book!





